What Is End to End Testing a Complete Guide
When we talk about end-to-end testing, we're asking one simple but crucial question: "Does our application actually work for a real person, from the moment they start until they finish what they came to do?"
It’s about simulating a complete user journey, putting the entire software system—with all its interconnected parts—through its paces to make sure everything flows just as it should.
Understanding the Full User Journey

Imagine you’re building an e-commerce website. Other types of testing look at the individual components. A unit test might confirm that the "Add to Cart" button works on its own. An integration test might check that the shopping cart can talk to the payment processor.
But neither of those tests can guarantee a customer can actually buy something. That's where end-to-end (E2E) testing comes in.
E2E testing validates the entire process as one continuous workflow. Think of it as the ultimate test drive for your application. It mimics exactly what a user would do and answers the big-picture questions:
- Can someone find a product, add it to their cart, and proceed to checkout?
- If they enter a discount code, does the total update correctly?
- Does the payment go through, the inventory get updated, and the confirmation email actually get sent?
This holistic view is absolutely essential for today's complex applications. Most apps aren't just one monolithic block of code; they're a web of databases, third-party services, and intricate API interactions. A single broken link in that chain can derail the whole user experience. If you want to dive deeper into those connections, our guide on what is API testing is a great place to start.
Ultimately, E2E testing serves as the final quality checkpoint, making sure all those moving parts are playing nicely together.
Before we go further, let's quickly summarize the core ideas behind E2E testing.
Core Concepts of End to End Testing at a Glance
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| User Journey Simulation | Mimics real-world user paths and workflows from start to finish, not just isolated functions. |
| System-Wide Scope | Tests the entire application stack, including the UI, backend services, databases, and external APIs. |
| Data Integrity | Verifies that data flows correctly and consistently through all interconnected systems during a workflow. |
| Business Logic Validation | Confirms that the application meets business requirements and delivers the intended value to the user. |
This table shows how E2E testing is about more than just code—it’s about validating the complete user experience and business process.
The Role of Automation in E2E Testing
Let's be honest: E2E tests can be complex and take a lot of time to run. This is why you'll often see them placed at the top of the classic testing pyramid, reserved for the most critical paths.
However, modern automation tools have changed the game, making these tests faster and more accessible. Today, most teams have found a happy medium. In fact, a study mentioned in the Microsoft engineering playbook found that about 70% of organizations now use a blend of automated and manual E2E tests. This approach gives them the broad coverage of automation combined with the insightful, exploratory nature of human testing.
End-to-end testing isn't just about finding bugs; it's about verifying business logic. It confirms that the software delivers the value it promised to the end user, from the first click to the final confirmation.
This approach delivers the highest level of confidence that your system is ready for the real world. It protects your brand’s reputation and your bottom line by catching those critical, workflow-breaking bugs before they ever reach your customers.
How E2E Testing Became an Industry Standard

In the early days of software, things were a lot simpler. An application was often a single, self-contained program. You could test its parts in isolation, and if every piece worked, you could be pretty confident the whole thing would, too. That approach worked just fine for a while, but technology didn't stay simple for long.
Applications started to evolve. They morphed from standalone tools into sprawling, interconnected ecosystems. A modern app is often a complex web of microservices, databases, third-party APIs, and user interfaces, all of which have to communicate perfectly. This new reality created a new kind of risk: individual components could pass every isolated test with flying colors but still cause the entire system to crash when they tried to interact.
The Rise of Interconnected Systems
It became obvious that we needed a way to test the entire workflow, not just the pieces. End-to-end testing emerged in the early 2000s to solve this exact problem. Development teams finally had a way to verify that a complete business process—like a customer successfully making an online purchase—worked flawlessly from start to finish.
By 2010, the practice was no longer a niche strategy. Industry reports showed that over 70% of enterprise projects were using some form of end-to-end testing to make sure their systems held up under real-world conditions. For a deeper look at this journey, the history of E2E testing methodologies on TechTarget is a great resource.
The push toward Agile and DevOps only accelerated this trend. With teams pushing code faster and more frequently, they desperately needed an automated safety net to catch system-wide failures before they hit production. End-to-end testing became that final, critical checkpoint.
End-to-end testing evolved from a "nice-to-have" to a "must-have" because modern applications are no longer islands. They are continents connected by countless digital bridges, and E2E testing is the only way to ensure traffic flows smoothly across all of them.
Horizontal vs. Vertical E2E Testing
As teams got more experienced with E2E testing, two main strategies took shape: horizontal and vertical. Knowing when to use each one is key to getting the most out of your testing efforts.
Horizontal E2E Testing: Think of this as the classic, wide-angle view. You're testing a complete user journey as it cuts across the entire system. A horizontal test follows a user from their very first click to their final goal, touching multiple applications and services along the way. A perfect example is testing an e-commerce flow: a user browses products, adds an item to their cart, completes the checkout, pays, and gets a confirmation email.
Vertical E2E Testing: This approach is all about depth, not breadth. Instead of following a user journey across different apps, you're doing a deep dive into a single, specific feature or technical stack within one application. For instance, a vertical test might focus solely on the payment processing system, testing every single layer from the UI fields down to the database transactions and the API calls made to the payment gateway.
So, which one should you use? It really depends on your goal. Horizontal testing is fantastic for validating the overall business flow and ensuring a great user experience. Vertical testing, on the other hand, is your go-to for confirming the rock-solid technical integrity of a critical system component. Using a mix of both gives you a powerful way to ensure total system quality.
E2E Testing vs. Other Common Test Types
To really get a feel for what end-to-end testing is, it helps to see how it stacks up against other types of software testing. Think of it this way: inspecting a car’s engine is important, but you wouldn't buy it without a test drive. Different tests look at your application from different angles, each with a very specific job.
Let’s use the analogy of building a house. Every stage of construction needs its own quality check, and software is no different. You wouldn't just check the plumbing and assume the electrical wiring is fine.
A Look at Different Testing Levels
We can map the most common testing methods to the quality checks you'd perform on that new house:
Unit Testing: This is like checking individual bricks or electrical outlets. Does a single light switch work? Does the faucet turn on and off? Unit tests focus on the smallest pieces of your application—a single function or method—to make sure each one works perfectly on its own.
Integration Testing: Now we're checking how those individual pieces work together. Do all the outlets in one room connect properly to the circuit breaker? When you flush the toilet, does it pull water from the main plumbing line as expected? Integration tests confirm that different modules or services can talk to each other without falling apart.
Functional Testing: This stage checks if specific features meet business requirements. For instance, does the thermostat correctly regulate the temperature in the living room? Does the garage door opener work from the remote? Functional tests are about verifying that a specific feature does what it's supposed to do, often in isolation from the full user journey.
End-to-End (E2E) Testing: This is the full, final walkthrough before the new owners move in. It mimics a real-life scenario from start to finish. Can you turn on all the lights, run the dishwasher, and use the microwave at the same time without tripping a breaker? E2E testing validates an entire user workflow, ensuring all the integrated parts work together to deliver the experience your users actually expect.
This image gives a great visual breakdown of how these testing types differ in scope and complexity.
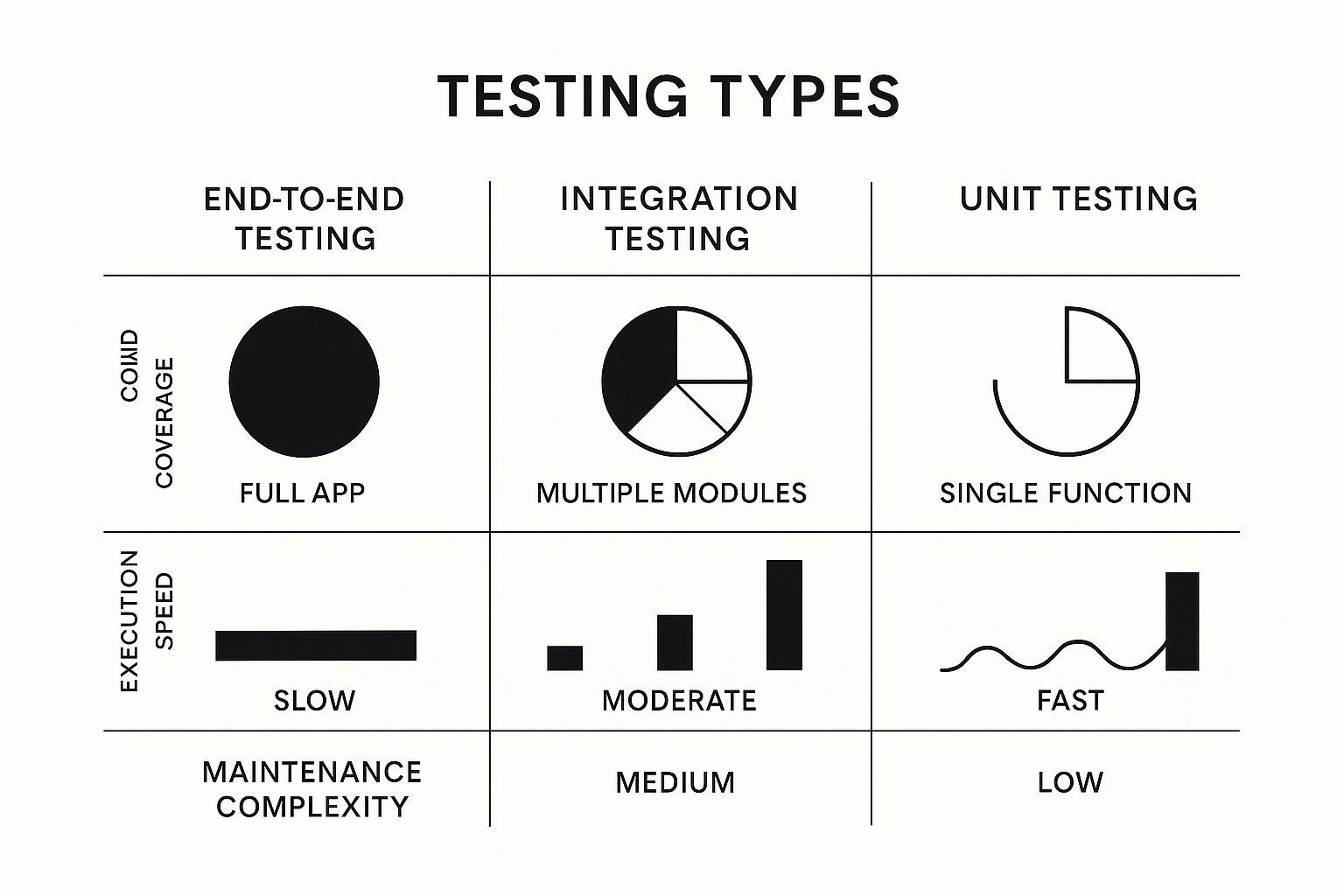
As you can see, as the test scope gets bigger, the tests themselves become more complex and take longer to run.
To make these distinctions even clearer, here’s a quick side-by-side comparison.
Comparison of Software Testing Types
| Testing Type | Scope | Primary Goal | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | A single function, method, or component. | Verify that the smallest piece of code works correctly in isolation. | Checking if a calculateTotal() function returns the correct sum. |
| Integration Testing | Two or more connected modules or services. | Ensure that different parts of the application can communicate and exchange data. | Verifying that the payment gateway successfully processes an order from the cart service. |
| Functional Testing | A specific feature or business requirement. | Confirm that a feature behaves according to its specifications. | Testing the "add to cart" button to ensure it adds the correct item and quantity. |
| End-to-End Testing | The entire application workflow, from start to finish. | Validate the complete user journey across all integrated systems. | Simulating a user logging in, searching for a product, adding it to the cart, and checking out. |
This table shows how each testing type has a unique role, from the microscopic view of unit tests to the panoramic view of E2E testing.
Building a Balanced Testing Strategy
While E2E tests give you the most confidence that everything is working, they are also the slowest and most brittle. Relying only on them would be a huge bottleneck for your team.
A smart QA strategy doesn’t pick one test type over another—it uses them all in a balanced way.
Unit and integration tests are your first line of defense. They are fast, cheap to run, and catch bugs right at the source code level. End-to-end tests then come in to provide that final, crucial validation of the complete user experience.
By combining these approaches, you create a multi-layered defense against bugs. Small issues get caught early by fast, focused tests, which frees up your more resource-intensive E2E tests to focus on what they do best: confirming your critical business flows work exactly as they should in the real world.
The Business Case for End to End Testing
While end to end (E2E) testing is a technical process, its real impact is measured in business results. These tests step beyond individual lines of code to look at the entire customer experience. Think of them as the final, most important safety check before you push a release live.
This is where you get the ultimate confidence that a new feature or bug fix hasn't accidentally torpedoed a critical user journey somewhere else in the application. That kind of validation is priceless for protecting your brand's reputation—it stops users from hitting show-stopping bugs that kill trust and send them looking for an alternative.
Imagine a customer trying to check out on your e-commerce site, only for the payment process to fail without explanation. That's not just a bug; it's a lost sale. E2E tests are designed to catch exactly these kinds of frustrating, multi-system failures that destroy conversions.
Reducing Costs and Accelerating Releases
By mimicking what a real user does, you can uncover complex bugs much earlier in the game, long before they ever see the light of day in production. Everyone knows that fixing a bug in a live environment is exponentially more expensive and stressful than catching it during the testing phase. The numbers back this up.
A 2023 industry report revealed that organizations with solid E2E testing strategies cut their critical post-release defects by an incredible 45%. The same report found they slashed the average time to find major bugs by 30%, which in turn helped them speed up their release cycles by an average of 20%. You can dig deeper into these findings on E2E testing efficiency.
Investing in end to end testing isn't just another line item on a budget. It's a direct investment in customer satisfaction, brand integrity, and the long-term financial health of your business. It shifts the entire team's focus from frantically fixing problems to preventing them in the first place.
When you get it right, a strong E2E testing strategy creates a positive feedback loop that helps the whole company:
- Product Teams can see that the software truly meets business goals and delivers the value they envisioned for users.
- Marketing Teams can rest easy knowing the brand's reputation is protected by a smooth, professional user experience.
- The Bottom Line is shielded from revenue loss caused by broken checkout flows or other critical paths, not to mention the high cost of emergency hotfixes.
How to Overcome Common E2E Testing Hurdles
Let's be honest: while end-to-end testing is incredibly powerful, it's rarely a walk in the park. It comes with its own set of challenges that can trip up even seasoned development teams. But knowing what you're up against is half the battle.
The most common headaches are chaotic test environments, infuriatingly flaky tests, and execution speeds that feel like they're moving at a snail's pace. The good news? With the right approach, you can get these problems under control.
Taming Test Environment Chaos
One of the biggest struggles is just getting a stable test environment up and running. To be effective, this environment has to perfectly mimic production, with every backend service, database, and third-party API available and playing nicely together. If even one of those components goes down or is misconfigured, your entire E2E test suite can light up with failures, sending your team on a wild goose chase for a bug that isn't even there.
The solution is to get smarter about how you manage these environments.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation are game-changers here. They let you define your entire test environment in code, making it completely repeatable. You can spin up a perfect, consistent environment on demand and tear it down when you're done.
- Service Virtualization and API Mocking: Do you really need to hit the live third-party payment gateway every time you run a test? Probably not. Tools like dotMock let you create a stand-in—a "mock"—of these external services. This gives you total control over their behavior and ensures they're always available. This is a core tactic for anyone learning how to test REST APIs without the external dependencies.
Conquering Test Flakiness
We've all been there. A "flaky" test is one that passes, then fails, then passes again, all without any changes to the code. This is the fastest way to make your team lose faith in your test suite. The culprit is rarely a real bug; it’s usually something like a network hiccup, an unexpected animation, or an element taking a fraction of a second too long to load.
A flaky E2E test is worse than no test at all. It erodes confidence, wastes developer time investigating non-existent issues, and eventually leads to the entire test suite being ignored.
The trick is to build more resilient tests. Stop using fixed delays like "wait for 5 seconds." That's a recipe for disaster. Instead, build intelligent waits into your scripts. Tell your test to wait until the button is visible and clickable, no matter how long that takes. This simple shift makes your tests far more adaptable to real-world conditions.
Accelerating Slow Execution Speeds
Finally, there's the speed problem. E2E tests are thorough, which means they are inherently slow. Running a full suite can take hours, which can bring a fast-moving CI/CD pipeline to a screeching halt.
You have to be strategic. You can’t run every single E2E test on every single code commit. Instead, try this tiered approach:
- Run a Smoke Test: For every commit, trigger a small, vital set of tests that cover the absolute must-have functionality, like user login or adding an item to a cart. These should be fast.
- Run the Full Suite Nightly: Schedule the whole time-consuming E2E suite to run overnight. This way, you get the full picture without blocking developers during the day.
- Parallelize Execution: Don't run your tests one by one. Use cloud testing grids to run dozens of tests at the same time. This can slash your total execution time from hours down to minutes.
Proven Best Practices for E2E Testing

Running a successful end-to-end (E2E) testing strategy isn't just about picking the right tools—it’s about having a disciplined process. Following a few battle-tested best practices can turn a chaotic, flaky test suite into a reliable quality gate that gives your team real confidence before every single release.
The first, and most important, step is to focus your energy where it actually counts. Don't try to test every imaginable user path. Instead, laser-focus on the critical user journeys that are the lifeblood of your business.
Prioritize Critical User Journeys
Let's be honest: not all user workflows are created equal. A glitch in the "update profile picture" feature is an annoyance. A failure in the checkout process? That could cost you thousands in lost revenue in just a few minutes.
Your team's time is precious. Start by identifying and automating tests for these high-impact scenarios first.
To do this right, you should:
- Identify Revenue-Critical Paths: Get granular. Map out the exact sequence of clicks and inputs a user takes to complete a purchase, sign up for a subscription, or take another core action.
- Focus on High-Traffic Features: Dive into your user analytics. Which parts of your application get the most traffic? Those are the areas that need to be absolutely bulletproof.
- Assess Business Risk: Think about what could go wrong. Which failures would do the most damage to your brand’s reputation or your bottom line?
When you concentrate on these vital flows, your E2E tests deliver the biggest bang for your buck by protecting the most important parts of your user experience.
"A well-prioritized E2E test suite acts as a guardian for your business logic. It doesn't just check for code errors; it confirms that your application can still deliver value to your customers, even after significant changes."
Isolate Tests and Manage Data
Another pillar of dependable E2E testing is isolation. Each test should be a self-contained universe, able to run on its own without needing the state left behind by a previous test.
When tests depend on each other, a single failure creates a confusing domino effect, making it a nightmare to find the real source of the problem.
This means every test needs to manage its own data setup and cleanup. For instance, a test for user registration should create a new, unique user every single time it runs and then remove that user from the database when it’s done. This simple practice prevents data conflicts and guarantees consistent, repeatable results.
Building solid systems always comes down to following clear guidelines. If you want to dive deeper, exploring API development best practices offers great insights into creating stable, testable services. Ultimately, these testing habits should be part of a larger push for quality assurance process improvement across your entire team.
Your Top E2E Testing Questions, Answered
Alright, even when you have a good handle on the basics, the practical questions always pop up once you start rolling up your sleeves. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that teams run into when they're getting started with E2E testing.
How Do We Choose Which User Flows to Test First?
This is a big one. With so many potential user journeys, staring at a blank slate can feel paralyzing. The trick is to stop thinking about testing everything and start thinking about protecting what matters most.
Your first move should be to identify the revenue-critical paths. Think about it: what are the absolute, must-work-or-we-lose-money workflows? For an online store, it's the full "add to cart to successful payment" journey. For a SaaS product, it’s probably the new user signup and subscription flow. Nail these down first; they’re the lifeblood of the business.
After that, look at your analytics. Where do most of your users spend their time? Those high-traffic features are your next priority. A bug in a rarely used corner of the app is a nuisance, but a bug in a core, daily-use feature is a five-alarm fire affecting the majority of your user base.
Can End-to-End Testing Be Fully Automated?
Technically, yes, you can automate just about any E2E test. But the real question is, should you? The most effective strategy is almost never 100% automation.
Automation is an absolute workhorse. It's brilliant for running those critical-path tests over and over again inside your CI/CD pipeline, ensuring your core functionality never breaks. Think login processes, checkout flows, or other predictable, high-value scenarios. It’s consistent, fast, and tireless.
But automation has a blind spot: it can't think outside the box. It will only ever test what you tell it to. This is where manual, exploratory testing shines. A human tester can get creative, poke around in weird ways, and spot usability quirks or odd edge cases that a script would just plow right past. The best results always come from a healthy mix—let automation handle the repetitive heavy lifting, and let humans do the clever, intuitive discovery.
What Are Some Popular Tools for E2E Testing?
The tool landscape is packed with great options, so you can definitely find one that fits your team's stack and style. Here are a few heavy hitters you'll see mentioned all the time:
- Selenium: The original titan of browser automation. It’s been around forever, supports a massive range of browsers and programming languages, and has a huge community behind it.
- Cypress: A more modern, all-in-one framework that developers absolutely love. It’s known for making testing faster and more intuitive by running directly inside the browser.
- Playwright: Microsoft’s powerful entry into the space. Its big claim to fame is its ability to automate all major browser engines (Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit) with a single, clean API.
Struggling with flaky tests because a third-party API is down again? Managing external dependencies is one of the biggest headaches in E2E testing. With dotMock, you can spin up a stable, predictable mock API in just a few seconds. Isolate your system, kill the flakiness, and get back to shipping reliable code. Stop waiting on other people's services and take control at https://dotmock.com.