What is Shift Left Testing? Improve Quality & Prevent Bugs
At its core, shift left testing means moving testing activities much earlier in the software development process. Instead of treating testing as a final checkpoint before release, teams start testing right from the beginning—during design, planning, and coding. The focus shifts from just finding bugs to actively preventing them.
What is Shift Left Testing, Really?
Think about building a house. The old way of testing software is like waiting until the house is completely finished—paint, roof, plumbing, everything—before you check the foundation. If you find a major crack at that point, the cost and effort to fix it are astronomical. It’s a disaster.
Shift left testing is the common-sense alternative. It’s about checking the foundation before the concrete is even poured. It’s about inspecting the framing before the drywall goes up. You catch problems when they are small, simple, and cheap to solve.
That’s the essence of shift left testing. The term "shift left" was first introduced by Larry Smith back in 2001, and it literally means moving testing to the left on a typical project timeline diagram. Before this idea gained traction, most teams used a Waterfall model where testing was the final, stressful gate before a product could ship, which inevitably created huge bottlenecks. You can learn more about its origins from this deep dive on Codacy's blog.
A Fundamental Mindset Shift
Ultimately, shifting left is more than just a process change; it’s a culture change. It’s about making quality a shared responsibility for the entire team, not just a task for the QA department.
Developers, testers, and product managers all work together from the very start. This constant collaboration ensures everyone is on the same page about quality expectations and project goals, breaking down the silos that so often lead to problems down the road.
This is how shifting left connects directly to real business results.
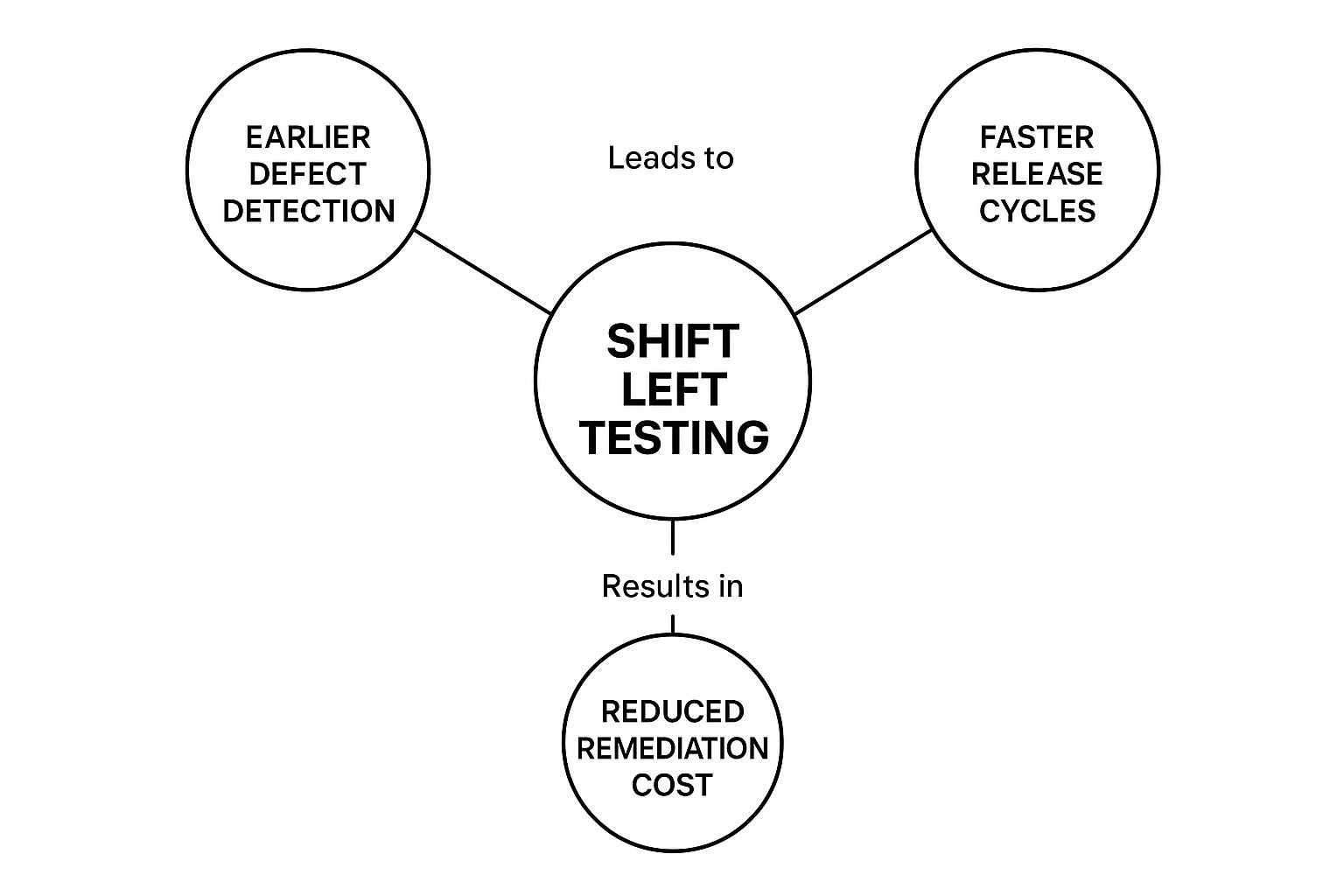
As the diagram shows, finding bugs earlier doesn't just save a little money—it dramatically lowers the cost to fix them and speeds up your entire delivery schedule.
"The goal of shifting left is not just to test earlier, but to build a culture where quality is inherent to the development process. It transforms testing from an event into a continuous, collaborative activity."
This approach turns a rigid, linear process into a dynamic cycle of building, testing, and getting feedback almost instantly. Early validation is key, but it doesn't mean you can skip the big picture checks. To see how it all fits together, check out our guide on what is end-to-end testing.
Traditional vs Shift Left Testing At a Glance
The difference between these two philosophies is night and day. This table breaks down exactly how they stack up.
| Aspect | Traditional (Waterfall) Testing | Shift Left Testing |
|---|---|---|
| When Testing Happens | At the very end of the development cycle, after coding is "complete." | Continuously, from the requirements and design phase onward. |
| Primary Goal | Find defects before the product ships to customers. | Prevent defects from ever being introduced in the first place. |
| Cost of Fixing Bugs | Extremely high, as issues are found late in the process. | Significantly lower, as issues are caught early and are simpler to fix. |
| Team Responsibility | Quality is owned solely by a dedicated QA or testing team. | Quality is a shared responsibility across developers, QA, and operations. |
| Feedback Loop | Very long; developers may not get feedback on their code for weeks. | Short and fast; feedback is provided almost instantly. |
| Development Process | Siloed and linear. Each team hands off work to the next. | Collaborative and iterative. Teams work together in a continuous loop. |
Seeing it laid out like this makes the benefits obvious. The traditional model sets teams up for last-minute crunches and expensive rework, while the shift left model fosters a proactive, efficient, and collaborative environment.
The True Cost of Finding Bugs Late

Waiting until the very end of the development cycle to test your software isn't just a bad habit; it's a massive business risk. When bugs surface right before a launch, they set off a chain reaction that goes way beyond a few lines of broken code. The pressure skyrockets, deadlines get blown, and the costs can spiral out of control.
Think about it this way. A simple miscommunication happens during the requirements phase for a new e-commerce feature. A developer, working from that flawed understanding, builds the entire component. Since no real testing is happening yet, that mistake gets baked deep into the codebase. Weeks go by. Then, in the final QA crunch, someone finally spots the bug.
By then, the damage is done. Fixing it isn't a quick patch. It means untangling dependencies, rewriting huge chunks of code, and then re-testing everything connected to that feature. What started as a tiny oversight has now become an expensive, time-consuming roadblock, threatening the entire release.
The Exponential Curve of Bug Fixes
The financial hit from this "test-at-the-end" approach is genuinely staggering. It’s a well-known fact in software engineering: finding and fixing a bug late in the process is exponentially more expensive than catching it early on.
The cost to fix a problem blows up the longer it sits there. Industry data suggests a bug that might cost $1,000 to fix during the initial design phase could easily cost over $100,000 if it's only discovered after the product is live. This dramatic jump highlights the huge gamble of traditional, late-stage testing. You can dig into more data on this and the four types of shift left testing to see just how steep that curve is.
So, where does all that money go?
- Increased Developer Hours: Engineers have to drop what they're doing and dive back into old code they haven't touched in weeks, trying to remember the context and track down the root cause.
- Complex Rework: A fix in one place can easily break something else. This means you have to run extensive regression tests to make sure the "solution" didn't just create a new set of problems.
- Delayed Revenue: Every day a release is pushed back is another day you're not earning the revenue that new feature was supposed to bring in.
- Reputational Damage: Even worse, if the bug slips into production, you're looking at angry customers, bad reviews, and a serious hit to your brand's credibility.
Beyond Budgets and Deadlines
The fallout from late-stage bug hunting isn't just about money. It breeds a stressful, reactive culture where teams are always putting out fires instead of building cool new things. This leads directly to developer burnout, sinking morale, and a pile-up of technical debt—those quick and dirty fixes made under pressure that make all future work slower and harder.
By delaying quality checks, organizations inadvertently choose a path of higher costs, missed deadlines, and frustrated teams. Shifting left is about breaking this cycle and building a proactive culture where quality is an enabler of speed, not an obstacle.
In the end, the true cost of finding bugs late is the lost opportunity to build better products, faster. And this is the fundamental problem that understanding what is shift left testing is all about solving.
The Pillars of a Modern Shift Left Strategy

Getting shift left right is about more than just buying new tools or tweaking a few steps in your process. It’s a genuine culture shift, one that rests on four core ideas. When these pillars work together, they create a development environment where quality isn't an afterthought—it's built in from the very beginning.
This isn't just a niche trend anymore. Recent studies show that over 70% of companies are now building testing into their earliest development stages. The payoff is huge, with teams reporting a 30-40% drop in bugs after release and getting their products to market 20-30% faster. If you want to dig deeper into the data, this article on Nothing Ventured Rocks offers some great insights.
Continuous Testing and Early Feedback
The first pillar is all about continuous testing. Forget the old model of having a separate, walled-off "testing phase." Here, quality checks are happening all the time, woven directly into the daily workflow. This creates a constant feedback loop, so teams can catch and squash issues almost as soon as they appear.
Think about it: a developer gets an instant notification about a potential bug or security flaw right in their code editor, moments after they’ve written the line. This is the reality when automated checks run on every single code commit.
This immediate feedback is a game-changer. It shrinks the time between writing code and seeing its real-world impact. Suddenly, fixing a bug isn't a week-long archeological dig; it’s a quick, five-minute fix.
Shared Ownership of Quality
In the old days, quality was the QA team's problem. A true shift left approach tears down that silo. Quality becomes everyone's job—developers, testers, product managers, and even the operations team.
In a shift left culture, quality is not a gate that code must pass through. It is a collective mindset and a core component of everyone's job description.
This is all about empowerment. Give developers the right tools and training, and they’ll start writing code that’s more secure, resilient, and easier to test from the get-go. The role of QA experts changes, too. They become quality coaches, helping the entire team level up its testing game instead of just hunting for bugs at the end.
Leveraging Smart Automation
Automation is what makes a shift left strategy hum. Let's be honest, you can't provide fast, continuous feedback if you're doing everything by hand. By automating the repetitive, predictable tests, teams can cover more ground, slash human error, and let their engineers focus on the tricky, creative problems that actually require a human brain.
This automation usually happens at a few key levels:
- Static Code Analysis: Tools that automatically scan code for common mistakes and vulnerabilities while it's being written.
- Unit and Integration Tests: Automated scripts that confirm individual code components work as expected and play nicely with each other.
- API and Contract Testing: Checks that make sure different microservices can communicate correctly long before they’re all deployed together.
These automated safety nets give teams the confidence to build and ship code quickly without worrying that they’re breaking things. This is where tools like dotMock become indispensable. By allowing you to mock APIs, you can test dependencies and edge cases right from the start, making this pillar not just a goal, but a reality.
How to Implement Shift-Left Testing in Your Workflow

Making the switch to a shift-left model is about more than just a new mindset; it requires practical, concrete changes at every single stage of your development lifecycle. The whole idea is to weave testing so tightly into your process that it’s just part of how you build software, not a gate you have to pass at the end.
Here’s a practical roadmap you can start following today to bring shift-left testing into your team’s workflow.
Start with Requirements and Design
Believe it or not, the earliest and cheapest place to catch a bug is before anyone has written a single line of code. Get your testers and QA pros into those initial requirements and design meetings. They have a knack for spotting ambiguities, contradictions, and weird edge cases that developers and product managers often overlook.
This is also the perfect time to bring in Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). When you write test scenarios in plain language (using a syntax like Gherkin), everyone gets on the same page. Developers, testers, and product owners all share a crystal-clear understanding of what a feature is supposed to do. This creates a living document that not only guides development but also becomes the blueprint for your automated tests later on.
Empower Developers with In-IDE Testing
The next move is to give developers tools that offer immediate feedback right as they're coding. This creates a super-tight feedback loop where problems are found and fixed in minutes, not days or weeks later during a formal QA cycle.
- Static Code Analysis: Plug tools like SonarLint directly into the IDE. Think of it as a powerful spell-checker for your code—it automatically flags potential bugs, security weak spots, and code style issues in real-time.
- Unit and Integration Testing: Build a culture where developers are expected to write and run unit tests for their own code. This proves that individual components work correctly in isolation. Following that up with early integration tests confirms that all those pieces can actually talk to each other without falling over.
A core principle of shift-left testing is making the right thing the easy thing. When you embed testing tools directly into the developer's daily workflow, quality stops being an afterthought and becomes a natural part of the coding process itself.
Test APIs and Dependencies Early
Modern software is all about APIs and microservices. The problem is, they can become massive bottlenecks if your team has to wait around for another team to finish building them. This is exactly where you can get clever and start testing dependencies that don’t even exist yet.
For instance, say the frontend team is ready to go but is blocked waiting on an API the backend team is still building. Instead of waiting, they can use a mock API to simulate its responses and keep moving forward.
This is where techniques like service virtualization really shine. You can test complex failure scenarios—like network timeouts or 500-error responses—long before anything gets deployed to a staging environment. To dig deeper, you can learn more about what is service virtualization from our detailed guide. Mastering this approach is key to understanding what shift-left testing really means in a modern, distributed system.
2. Your Essential Shift Left Toolkit
Shift-left testing isn't just a new way of thinking; it's a practice that hinges entirely on having the right tools for the job. You can't just tell your team to "test earlier"—you have to give them the technology that makes fast, automated feedback loops a reality. The right tools bake quality right into the development workflow, making it feel less like a chore and more like part of the process.
Think of it like a professional chef's kitchen. You wouldn't expect them to create a gourmet meal with just a single pan and a dull knife. They need a full range of specialized equipment, each one perfect for a specific task. Building great software is no different.
Foundational Code Quality Tools
The very first layer of defense in any shift-left toolkit is about the code itself. These tools are all about catching problems the instant they're written, acting like an over-the-shoulder code review that provides immediate feedback right inside the developer's editor.
Static Analysis (SAST): This is your front line. Tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx scan raw source code for potential bugs, security holes, and what we call "code smells" before the application is even compiled. They're fantastic for enforcing coding standards and stopping common errors from ever getting committed.
Unit Testing Frameworks: This is the bedrock of testing for developers. Frameworks such as JUnit for Java, PyTest for Python, or Jest for JavaScript let engineers write small, blazing-fast tests. These tests confirm that individual pieces of code—like a single function or component—work exactly as they should. A solid unit test suite gives everyone the confidence to make changes without worrying about breaking something else.
Simulating the Real World Early
One of the biggest roadblocks to testing early is dealing with dependencies. What do you do when the API your new feature needs to call isn't even built yet? This is where service virtualization and API mocking change the game, allowing teams to break free from dependencies and test complex situations from the get-go.
Service virtualization is what truly unlocks parallel development. It lets teams build and test against a stable, simulated version of a dependency, completely wiping out the bottlenecks and waiting games that slow everyone down.
This is precisely the problem platforms like dotMock were created to solve.
With an intuitive interface, developers can quickly spin up mock API endpoints and define their responses, simulating anything from a perfect data fetch to a frustrating network timeout. Using a tool like this means your team can test every possible scenario—good and bad—without ever needing a live backend service. Diving into strategies for testing in parallel can help you squeeze even more speed out of your delivery cycle.
To put it all together, here’s a quick look at the kinds of tools you’ll want to have in your shift-left arsenal.
Your Essential Shift Left Toolkit
A breakdown of key tool categories that support shift left testing, with examples and their primary use case in the development lifecycle.
| Tool Category | Primary Use | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Static Analysis (SAST) | Scans code for bugs and vulnerabilities as it's written. | SonarQube, Checkmarx |
| Unit Testing Frameworks | Verifies individual code components in isolation. | JUnit, PyTest, Jest |
| Service Virtualization | Simulates unavailable APIs and external dependencies. | dotMock, WireMock |
| CI/CD Platforms | Automates the build, test, and deployment pipeline. | Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions |
| Containerization | Creates consistent, portable testing environments. | Docker, Podman |
Having a mix of these tools doesn't just support a shift-left strategy—it makes it possible. They empower developers to own quality from the very start.
Common Questions About Shift Left Testing
Whenever teams start talking about shifting left, the same questions tend to pop up. That's perfectly normal. We're talking about a change that touches on team culture, individual roles, and long-standing processes.
Let's cut through the noise and answer the most common questions to help clear up any confusion.
Does Shift Left Testing Get Rid of the QA Team?
Not at all. In fact, it makes the QA team more valuable than ever, but their role definitely changes. The idea isn't to replace QA experts but to bring their skills into the development cycle much, much earlier.
Instead of being gatekeepers who just find bugs at the very end, they become quality coaches and strategic partners for the entire team.
In a healthy shift-left environment, QA professionals are the ones enabling everyone else to build quality in from the start. You'll see them:
- Building the test automation frameworks that developers rely on every day.
- Mentoring developers on how to write better, more thorough tests and think defensively about their code.
- Focusing on the big picture—mapping out complex test strategies, identifying high-risk areas, and planning for edge cases that go way beyond simple unit tests.
- Diving into exploratory testing, where their deep product knowledge lets them uncover the tricky, unexpected bugs that automated scripts will always miss.
Their focus moves from finding defects to actively preventing them. It's a fundamental shift that makes their expertise indispensable.
How Is Shift Left Different From Agile Testing?
This is a great question because the two are so closely related. The easiest way to think about it is that one is the philosophy, and the other is the practice that brings it to life.
Agile testing is the overarching philosophy of continuous testing that happens throughout an iterative development cycle. Shift left is the practical how-to—it’s the action of moving those testing activities as early as possible within each development sprint.
You can't really do Agile testing effectively without embracing shift-left principles. Agile says, "test continuously," and shift left answers, "by testing early and often."
What’s the Best First Step to Start Shifting Left?
Trying to change everything at once is a recipe for disaster. A fantastic, low-impact way to get started is by introducing static code analysis tools right into the developer's workflow.
Think of these tools as a powerful spell-checker for code. They run quietly in the background of the IDE and flag potential bugs, security weak spots, and code style issues as the developer is typing.
This is a perfect first step because it introduces the core principle of immediate feedback without disrupting your entire process. It’s an easy win that delivers immediate value and starts building that quality-first mindset from the ground up.
Can We Implement Shift Left in a Waterfall Environment?
Yes, absolutely. While shift left feels like it was tailor-made for Agile and DevOps, its core principle—"find problems earlier"—can bring huge benefits to any development model, including traditional Waterfall.
You don't have to change everything overnight. The goal is simply to move quality checks further to the left of wherever they are right now.
In a classic Waterfall or V-Model project, this could look like:
- Holding much more thorough reviews of requirements and design documents before a single line of code is written.
- Writing detailed test cases during the design phase, rather than waiting until the coding is finished.
- Expecting developers to run comprehensive unit and integration tests before they hand their work over to the QA team.
Ready to break down testing bottlenecks and accelerate your development cycles? With dotMock, your teams can create mock APIs in seconds, enabling true parallel development and robust testing from day one. Start mocking for free and ship faster with dotMock.