8 API Documentation Best Practices for 2025
In today's development ecosystem, API documentation is more than just a technical reference; it's the primary interface for your developer users. Good documentation accelerates adoption, reduces support overhead, and builds a loyal developer community. Great documentation, however, is a significant competitive advantage. It transforms a functional tool into an intuitive, delightful experience that empowers developers to build faster and more effectively.
This guide goes beyond the basics to explore the top API documentation best practices that separate world-class APIs from the rest. We will dive into actionable strategies, from creating interactive playgrounds and providing multi-language code examples to structuring information for effortless discovery. You'll learn how to craft clear authentication guides, comprehensive error handling references, and quickstart tutorials that get developers to their first successful API call in minutes.
By implementing these practices, you can build documentation that not only informs but also inspires, turning your API into an indispensable resource for frontend developers, QA teams, and software architects alike. Let’s explore how to create docs that developers actually love to use.
1. Interactive Documentation and Try-It-Out Features
Static documentation is a reference, but interactive documentation is an experience. This approach transforms a passive reading session into a hands-on lab, allowing developers to execute API calls directly from the browser. Instead of just reading about an endpoint, users can input parameters, send a live request to a sandboxed environment, and see the real-time response, including headers and status codes. This immediate feedback loop is one of the most effective api documentation best practices for accelerating developer onboarding.

The "try-it-out" feature removes the initial friction of setting up a local development environment or using a third-party tool like Postman just to make a test call. By embedding this functionality, you empower developers to validate their assumptions and understand your API's behavior instantly.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
Interactive docs significantly reduce the "time to first call," a critical metric for developer adoption. When a developer can successfully interact with your API within minutes of landing on your documentation, their confidence and engagement soar. This is particularly valuable for technical leads coordinating workstreams and startup teams building proofs of concept, as it allows for rapid experimentation without any setup overhead.
How to Implement It Effectively
To make your interactive documentation truly useful, focus on creating a realistic and safe testing environment.
- Use a Sandbox Environment: Crucially, ensure that all "try-it-out" requests are routed to a dedicated sandbox environment. This protects production data and services from accidental modifications or heavy load from documentation users.
- Provide Pre-filled Examples: Don't present developers with blank fields. Offer pre-populated, realistic sample data for request bodies and parameters. For an e-commerce API, a sample
product_idshould be a valid ID within the sandbox. - Clarify Authentication: Clearly explain how authentication works within the interactive console. Provide pre-generated, temporary API keys for the sandbox so users don't have to use their own production credentials.
- Display Rate Limits: Be transparent about any rate limits on the test environment to prevent abuse and manage user expectations. Add clear warnings about data persistence, letting users know if their test data will be cleared periodically.
This approach has been popularized by tools built around the OpenAPI Specification, such as Swagger UI and Redoc, which automatically generate interactive consoles. Companies like Stripe and Twilio are masters of this, providing polished API explorers that feel like integrated products themselves.
2. Comprehensive Code Examples in Multiple Languages
While API reference guides detail what an endpoint does, developers need to know how to use it in their specific tech stack. Providing complete, copy-paste-ready code examples in multiple popular programming languages is a cornerstone of effective API documentation. This goes beyond showing a simple cURL command; it means offering idiomatic, runnable snippets for languages like Python, JavaScript (Node.js), Java, Ruby, and PHP that developers can drop directly into their codebase.

This practice bridges the gap between theory and implementation, saving developers from the tedious and error-prone process of manually translating HTTP requests into their preferred language's syntax. It's a critical component of strong api documentation best practices because it directly accelerates the integration process.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
Multi-language code examples lower the barrier to entry for a diverse audience of developers. A frontend developer using JavaScript, a data scientist using Python, and a backend engineer using Java can all find immediate value without having to context-switch. This demonstrates that you understand and cater to your users' workflows, fostering goodwill and significantly boosting API adoption rates. Companies like SendGrid and AWS excel here, offering extensive libraries of examples for their SDKs and APIs.
How to Implement It Effectively
To ensure your code examples are truly helpful, they must be practical, reliable, and easy to use.
- Provide Runnable, Complete Snippets: Examples should include everything needed to run, such as necessary imports and basic variable initializations. Use clear placeholders like
YOUR_API_KEYfor values the user must provide. - Include Error Handling: Don't just show the "happy path." Demonstrating how to properly catch and handle potential API errors (e.g., 404 Not Found, 401 Unauthorized) provides immense value and helps developers build more resilient applications.
- Keep Examples Updated: Programming languages and their popular libraries evolve. Regularly review and update your code samples to reflect the latest versions and best practices to avoid frustrating developers with outdated or deprecated code.
- Cover Real-World Use Cases: Instead of a generic
GET /items, show a more complex, realistic workflow. For instance, an e-commerce API could show a sequence for creating a cart, adding an item, and proceeding to checkout.
Tools like Postman and Insomnia have popularized this by automatically generating code snippets from API requests. Integrating a similar feature directly into your documentation ensures a seamless and efficient developer experience.
3. Clear Authentication and Authorization Documentation
Authentication is the first hurdle a developer must overcome to use your API. If this process is confusing, poorly documented, or error-prone, you risk losing potential users before they make their first successful call. Detailed, clear documentation of authentication mechanisms and authorization flows is one of the most fundamental api documentation best practices for building trust and ensuring a smooth developer onboarding experience.
This part of your documentation should act as a step-by-step guide, leaving no room for ambiguity. It must clearly explain how to obtain credentials, which authentication methods are supported (e.g., API Keys, OAuth 2.0, JWT), and how to correctly include them in a request. Neglecting this crucial step is like giving someone a key but not telling them which door it opens.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
Clear authentication documentation directly impacts the "time to first call" and developer confidence. When a developer can securely connect to your API on their first attempt, it sets a positive tone for the entire integration process. This is especially critical for technical leads and DevOps engineers who need to provision access securely and efficiently across different environments. A well-documented process minimizes support tickets and reduces friction.
The following infographic illustrates the typical three-step flow for token-based API authentication.
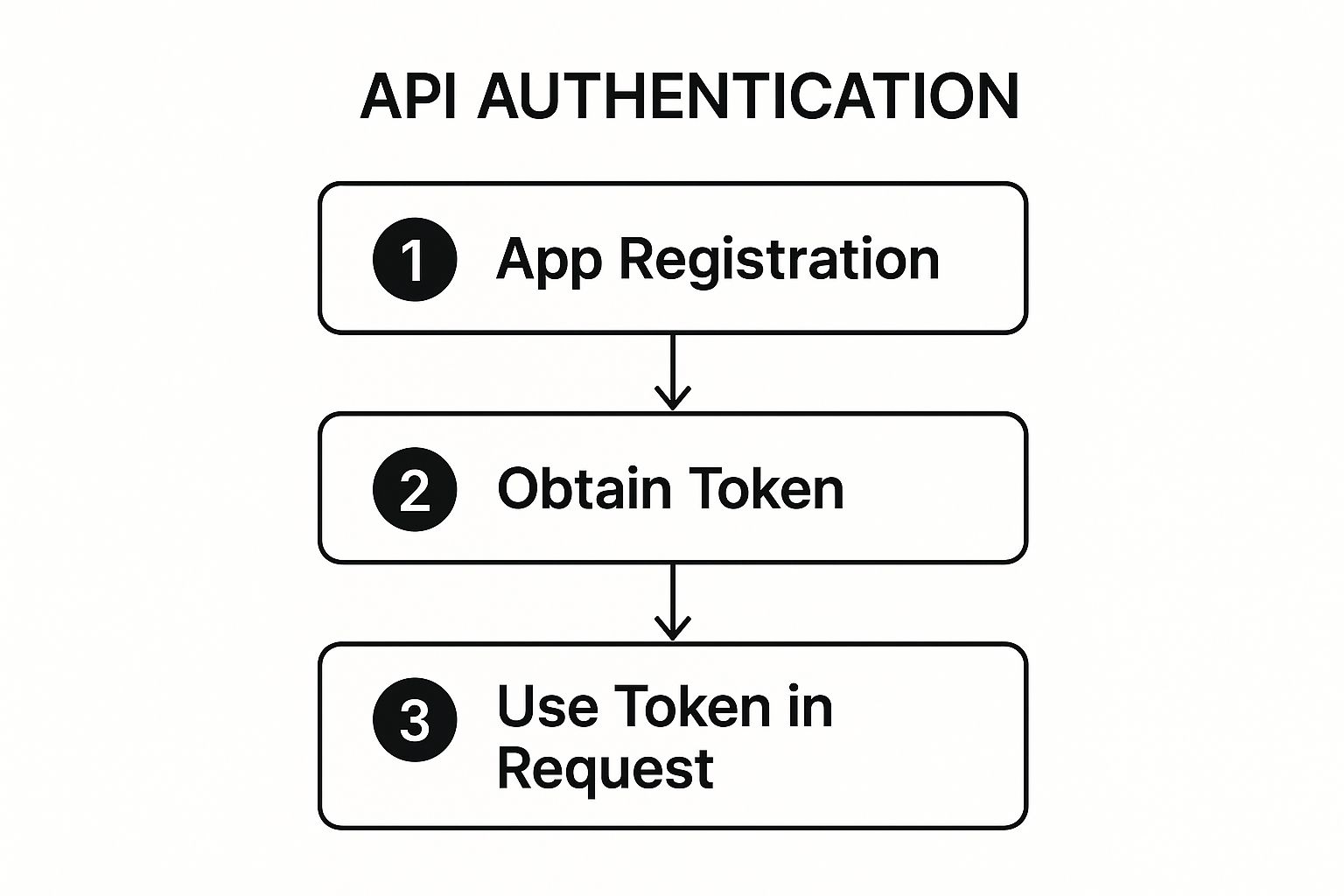
This simple, sequential process forms the basis of many modern authentication schemes, making it essential to document each stage clearly.
How to Implement It Effectively
To create effective authentication and authorization guides, focus on clarity, completeness, and practical examples.
- Provide Visual Flowcharts: For complex flows like OAuth 2.0, use diagrams to illustrate the sequence of redirects, token exchanges, and user consent steps. This helps developers visualize the entire process.
- Include Common Error Scenarios: Document common authentication errors (e.g.,
401 Unauthorized,403 Forbidden) and provide clear, actionable solutions for each. This helps users self-diagnose and resolve issues quickly. - Separate Basic and Advanced Topics: Structure the documentation to cater to different needs. Start with a simple API key guide for quick starts, then offer detailed sections on advanced topics like scope management and refresh tokens for those who need them.
- Regularly Audit Security Recommendations: Security best practices evolve. Regularly review and update your recommendations to protect your users and your platform. Learn more about essential API security practices on dotmock.com.
Companies like Google and Auth0 excel at this, offering comprehensive guides with code snippets in multiple languages, interactive diagrams, and detailed explanations of permissions and scopes. Their documentation empowers developers to implement secure authentication with confidence.
4. Comprehensive Error Handling Documentation
An API is only as reliable as its error handling, and documentation is the key to making that handling predictable. Comprehensive error documentation goes beyond simply listing HTTP status codes; it provides a full glossary of potential failure scenarios, complete with clear messages, custom error codes, and actionable troubleshooting steps. This turns a frustrating bug-hunt into a guided debugging session, saving developers hours of guesswork. Documenting what happens when things go wrong is one of the most crucial api documentation best practices for building trust and resilience.
This approach anticipates developer pain points. Instead of a generic 400 Bad Request that leaves a developer wondering if the issue is a missing parameter, invalid JSON, or a malformed header, detailed error docs provide specific error objects in the response body that pinpoint the exact problem.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
Thorough error documentation is fundamental for building robust applications. It empowers developers, especially QA and SRE teams, to code defensively and handle failure gracefully. When a developer can anticipate specific error types, they can write logic to retry a request, alert a user with a helpful message, or failover to a backup system. This level of detail transforms your API from a black box into a predictable, debuggable partner in their application stack.
How to Implement It Effectively
To create error documentation that actively helps developers, focus on clarity, context, and solutions.
- Provide Full Error Response Examples: For every documented error, show the exact JSON response body developers can expect. Include the custom error codes, human-readable messages, and any other relevant fields, like a
request_idfor support tickets. - Group Errors Logically: Organize errors by endpoint or by type (e.g., Authentication Errors, Validation Errors, Rate Limit Errors). This helps developers quickly find relevant information without sifting through a giant, unordered list.
- Offer Actionable Solutions: Don't just describe the problem; explain how to fix it. If an error is
invalid_api_key, the solution should be "Check that your API key is correct and has not expired. You can generate a new key in your dashboard." - Explain HTTP Status Codes: Clearly map your custom error codes to standard HTTP status codes. Explain why a particular action results in a
403 Forbiddenversus a401 Unauthorized, as the distinction is critical for security and access control logic.
Industry leaders like Stripe and Shopify excel at this, providing exhaustive error references that are as meticulously maintained as their success-path documentation. Their guides are a masterclass in turning potential developer frustration into a learning opportunity.
5. Logical Information Architecture and Navigation
An API can be feature-rich, but if developers can't find the information they need, its power is lost. Logical information architecture organizes your documentation into a coherent, intuitive structure that guides users to solutions. This goes beyond a simple list of endpoints; it involves creating a clear hierarchy, logical content grouping, and seamless navigation that helps developers find what they need quickly, whether they are just getting started or debugging a complex issue. Adopting a user-centric structure is a core principle of effective api documentation best practices.
A well-designed architecture anticipates the developer's journey. It separates "Getting Started" guides from deep API references and organizes endpoints into logical categories like "User Management" or "Billing." This prevents information overload and makes the documentation feel less like a dense textbook and more like a helpful map.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
Strong information architecture dramatically reduces cognitive load and search time. When developers can predict where to find information, they spend less time searching and more time building. This is especially critical for large, complex APIs where a flat list of endpoints would be overwhelming. For technical leads and architects, this means their teams can self-serve more effectively, reducing dependency on support channels and accelerating development cycles.
How to Implement It Effectively
Building an intuitive structure requires thinking like your users and providing multiple pathways to the same information.
- Organize by User Journey: Structure content logically from initial setup to advanced use cases. Start with authentication and quick-start guides, then move to core resources, and finally, cover specialized topics like error handling, webhooks, and versioning. You can explore more about managing different API versions in our guide to API versioning best practices on dotmock.com.
- Implement Robust Search: A powerful, facet-based search is non-negotiable. Allow developers to filter results by tutorials, API references, or error codes to pinpoint information instantly.
- Use Clear Categorization: Group related endpoints under intuitive headings. Spotify’s API, for instance, groups endpoints into categories like "Playlists," "Artists," and "Search," making it easy to find relevant functionality.
- Provide Contextual Navigation: Use breadcrumbs, a persistent sidebar, and in-page navigation to help developers understand their location within the documentation. Atlassian excels at this, providing a clear map of its extensive developer ecosystem.
6. Getting Started Guide and Quickstart Tutorials
While comprehensive endpoint references are essential, they can be overwhelming for new users. A "Getting Started" guide or a quickstart tutorial acts as a guided tour, streamlining the onboarding process to get developers from zero to their first successful API call as quickly as possible. This approach prioritizes momentum and confidence-building over exhaustive detail, offering a minimal viable example that delivers an immediate win. This is a cornerstone of modern api documentation best practices.

The goal of a quickstart is to reduce "time-to-hello-world," the API equivalent of a developer's first successful interaction. By providing copy-paste-ready code snippets, simple setup instructions, and a clear success metric, you eliminate initial friction and prove the value of your API within minutes, not hours.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
A well-crafted quickstart guide is one of the most powerful tools for developer adoption. It caters to users who learn by doing, allowing them to see tangible results without first needing to read every page of your documentation. For technical leads evaluating multiple APIs, a quick and successful first experience can be the deciding factor. This principle isn't just for APIs; any technical product benefits from having a clear download and installation guide to get users started smoothly.
How to Implement It Effectively
To create a quickstart guide that truly accelerates onboarding, focus on simplicity, clarity, and validation.
- Define a Single, Clear Goal: Focus the tutorial on a single, core use case, like sending a first message or creating a first user. Avoid introducing complex or optional parameters.
- Provide Copy-Paste Code: Offer complete, working code snippets for multiple popular languages. Ensure these snippets include everything needed to run, including authentication placeholders.
- Include Validation Steps: Don't just tell developers to run the code; tell them how to verify it worked. This could be checking their account dashboard, querying another endpoint, or looking for a specific response code.
- Time the Experience: Test how long it takes a new developer to complete the guide. Aim for 5-10 minutes. If it takes longer, simplify the steps.
This strategy has been perfected by leading developer-first companies. Twilio's 5-minute quickstarts are legendary for their simplicity, while Stripe's "Accept a Payment" tutorial walks users through a complete, real-world workflow.
7. Comprehensive API Reference with Schema Documentation
While getting started guides provide the narrative, a comprehensive API reference is the dictionary. This is the technical source of truth, meticulously detailing every endpoint, method, parameter, header, and response code. It goes beyond basic descriptions to include explicit data schemas, defining the exact structure, data types, and constraints for all request and response bodies. This level of detail is a cornerstone of effective api documentation best practices, eliminating ambiguity for developers.
A complete reference acts as a contract between your API and its consumers. When a developer needs to know the exact format of an error response or the validation rules for a specific field, the reference provides a definitive answer. It empowers QA teams to design thorough test cases and allows backend and frontend developers to work in parallel with confidence, knowing what data structures to expect.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
A detailed API reference minimizes guesswork and reduces support tickets. When developers can self-serve precise technical information, they can build more resilient integrations faster. This is invaluable for technical leads architecting systems and QA engineers creating edge-case scenarios, as it provides the granular detail needed for robust planning and testing. It serves as the foundation for both human understanding and machine automation.
How to Implement It Effectively
Creating a truly comprehensive reference requires discipline and a focus on clarity.
- Generate from Code: The most reliable way to maintain accuracy is to auto-generate your reference documentation directly from your API's source code or specification files, like an OpenAPI (Swagger) definition. This ensures the docs are always in sync with the actual API behavior. You can import an OpenAPI specification to streamline this process and keep your reference up-to-date.
- Include Validation Rules: Don't just list data types; specify constraints. Document required fields, string length limits (
min_length,max_length), numeric ranges (minimum,maximum), and accepted enum values. - Provide Full Schemas: Display the complete JSON or XML schema for every request and response body. This allows developers to understand nested objects and complex data structures at a glance.
- Use Consistent Terminology: Ensure that terms like
user_idoraccountIdare used consistently across all endpoints and models. A glossary of common terms can be a powerful addition.
This approach has been perfected by platforms that manage vast and complex APIs. The GitHub REST API reference is a prime example, offering exhaustive detail for every endpoint. Similarly, the Google Cloud and Slack API documentation provide model schemas and method specifications that leave no room for interpretation.
8. SDK and Tool Documentation Integration
An API is more than just its endpoints; it's an entire ecosystem of tools that developers use to build applications. Integrating documentation for Software Development Kits (SDKs), client libraries, and other development tools directly into your API reference is essential. This approach provides a holistic view, showing developers not just what the API does, but how to use it efficiently within their preferred programming language and environment. This consolidation is a critical api documentation best practices for creating a frictionless developer journey.
By documenting your official SDKs alongside your API endpoints, you guide developers toward the most robust and supported integration path. It saves them from writing boilerplate code to handle HTTP requests, authentication, and error handling, allowing them to focus on their application's core logic. This significantly accelerates development and reduces the likelihood of common implementation errors.
Why It’s a Game-Changer
A well-documented tool ecosystem transforms your API from a standalone service into a comprehensive developer platform. It builds confidence by showing a commitment to supporting multiple languages and frameworks. For technical leads, this is invaluable as it allows them to quickly assess if the API provides first-party support for their team's tech stack, simplifying project planning and resource allocation.
How to Implement It Effectively
To create a truly useful tool-integrated documentation hub, focus on clarity, maintenance, and discoverability.
- Keep SDK Docs in Sync: The most critical rule is to ensure your SDK documentation is always updated in lockstep with API changes. A version mismatch can lead to broken integrations and immense developer frustration. Use automation to link API version releases with SDK updates.
- Provide Language-Specific Examples: Don't just link to a generic SDK repository. Embed code examples for your most popular SDKs directly within the endpoint documentation. Show developers how to make a specific API call using Python, Node.js, or Java.
- Clarify Official vs. Community Tools: Clearly distinguish between official, first-party SDKs and third-party or community-contributed libraries. While community tools are valuable, developers need to understand the support level they can expect for each.
- Include Migration Guides: When you release a new major version of an SDK or tool, provide a clear, step-by-step migration guide. This helps existing users upgrade smoothly and prevents them from being stuck on outdated, unsupported versions.
This practice is perfected by major cloud providers like AWS, whose documentation meticulously details SDKs for dozens of languages. Similarly, Stripe and Twilio excel by integrating their helper library documentation so seamlessly that it feels like a natural extension of their core API reference.
API Documentation Best Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interactive Documentation and Try-It-Out Features | High - requires complex infra 🔄 | Moderate - needs sandbox & tooling ⚡ | Faster API trial & validation 📊 | APIs needing quick testing and live feedback 💡 | Immediate feedback, increased engagement ⭐ |
| Comprehensive Code Examples in Multiple Languages | Medium - ongoing multi-codebase maintenance 🔄 | High - maintain examples in many languages ⚡ | Accelerated onboarding, reduced support 📊 | APIs with broad developer audience 💡 | Best practice demos, wide tech coverage ⭐ |
| Clear Authentication and Authorization Documentation | Medium - can be complex to explain 🔄 | Moderate - requires security expertise ⚡ | Reduced errors, trusted security 📊 | Security-critical APIs 💡 | Builds developer trust, prevents unauthorized ⭐ |
| Comprehensive Error Handling Documentation | Medium - requires constant updates 🔄 | Moderate - needs detailed troubleshooting guides ⚡ | Faster debugging, improved reliability 📊 | APIs with complex error scenarios 💡 | Reduces frustration, supports debugging ⭐ |
| Logical Information Architecture and Navigation | High - significant planning needed 🔄 | Low - upfront design effort ⚡ | Faster info retrieval, better engagement 📊 | Large, growing API documentation 💡 | Supports multiple user flows, scalable ⭐ |
| Getting Started Guide and Quickstart Tutorials | Low - simpler content but needs balance 🔄 | Low - focused minimal examples ⚡ | Quick first success, higher adoption 📊 | New users onboarding rapidly 💡 | Builds confidence quickly, positive first use ⭐ |
| Comprehensive API Reference with Schema Documentation | High - extensive detail and maintenance 🔄 | High - rigorous update and validation ⚡ | Authoritative source, supports advanced use 📊 | APIs requiring precise contract and tooling 💡 | Enables automation, comprehensive ⭐ |
| SDK and Tool Documentation Integration | Medium to High - requires coordination 🔄 | Moderate - keep SDKs & tools updated ⚡ | Faster dev with pre-built solutions 📊 | Ecosystem with multiple tools and SDKs 💡 | Reduces integration errors, ecosystem growth ⭐ |
Putting It All Together: Your Path to Exceptional Documentation
Navigating the landscape of API documentation best practices can seem daunting, but the journey from good to exceptional documentation is a strategic investment in your product's success. We've explored the critical pillars: interactive "Try-It-Out" features that bridge the gap between theory and practice, comprehensive code examples in multiple languages that meet developers where they are, and crystal-clear guides on authentication and error handling that eliminate common friction points.
The core takeaway is this: your API documentation is not merely a technical reference; it's a fundamental part of the developer experience. It serves as the primary interface for your API, acting as a teacher, a guide, and a problem-solver. A logical information architecture, paired with a robust Quickstart Guide, ensures developers can achieve their first "aha!" moment quickly, building momentum and confidence. Meanwhile, a detailed API reference and integrated SDK documentation provide the depth needed for complex, long-term projects.
From Good Practice to Great Product
Adopting these principles transforms documentation from a passive asset into an active catalyst for growth. When developers can self-serve, find answers effortlessly, and test endpoints without friction, the benefits ripple across the entire ecosystem.
- Reduced Support Load: Clear, comprehensive documentation directly translates to fewer support tickets and repetitive questions, freeing up your engineering team to focus on core product development.
- Faster Developer Onboarding: A streamlined learning curve means new users and team members can integrate your API and start building valuable applications in hours or days, not weeks.
- Increased Adoption and Retention: A superior developer experience becomes a competitive differentiator. Developers are more likely to choose, champion, and continue using an API that is easy to work with and well-supported by its documentation.
Your Actionable Next Steps
Embarking on this path doesn’t require a complete overhaul overnight. Start by auditing your current documentation against the practices outlined in this article. Identify one or two high-impact areas for improvement. Perhaps it's adding a "Try-It-Out" feature to your most popular endpoint or enriching your error code reference with actionable solutions.
As your documentation matures, remember that it is a living document. It must evolve in lockstep with your API. This continuous improvement cycle is a hallmark of excellent API-first companies and is closely tied to the broader best practices for API integration within complex systems. By treating your documentation as a product, you foster a community of empowered, successful developers who can unlock the full potential of your platform.
Ready to ensure your documentation perfectly mirrors your API's behavior, even before it's fully built? dotMock allows you to create high-fidelity mock APIs from your OpenAPI specifications, helping you test, validate, and write accurate documentation from day one. Elevate your developer experience by visiting dotMock and start building better documentation today.